icacls.exe is a useful command line tool that can be used to change the NTFS file system permission in older versions of Operating systems like Windows Server 2003, 2007, and Windows 7. The interesting part about icacls.exe is that it is also available in Windows 10 and 11.
You might be familiar with Windows Server 2003 as Microsoft’s serving operating system. As an update from Windows Server 2000, it packed in more stability, and it comes with an in-box command-line utility called Integrity Control Access Control List (ICACL). And this is where the icacls.exe comes into the picture.
icacls.exe is a command-line utility file available on Windows Server 2003, and also in Windows 11. It was released to replace the cacls command. The full form of iCACLS is Integrity Control Access Control List. Its primary function is to show or change discretionary access control lists (also known as DACLs) for specific file. Files in some directories also use the stored DACLs.
Quick Overivew
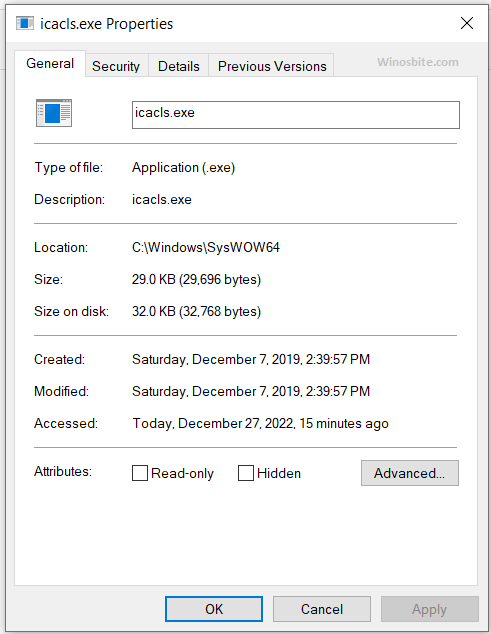
iCACLS File Location and Size
icacls.exe can be found in multiple locations in Windows 10 and 11 like under C:\Windows\System32; C:\Windows\SysWOW64; C:\Windows\WinSxS\ etc. Here is quick overview of this executable file:
- File Location: C:\Windows\System32
- File Size: 39kB (depending on your version and Windows build)
- Product Name: File version: 10.0.19041.1
The file includes a verified signature by Microsoft, but it does not have a visible window. Windows loads the file while booting. The security threats around the file are minimal, but you can easily verify whether it’s a maliciousness.
Icacls Syntax:
- For files to display DACLs:
icacls<filename> [/grant[:r] <sid>:<perm>[...]] [/deny <sid>:<perm>[...]] [/remove[:g|:d]] <sid>[...]] [/t] [/c] [/l] [/q] [/setintegritylevel<Level>:<policy>[...]]
- For directory to display DACLs:
icacls<directory> [/substitute <sidold><sidnew> [...]] [/restore <aclfile> [/c] [/l] [/q]]
The SID can also be alphanumeric. For numerical forms, all you have to do is to put a * as wildcard character to the beginning of SID.
Operations:
[/save <ACLfile> [/t] [/c] [/l] [/q]] – This function stores DACLs to an ACL file for matching files
/restore <ACLfile> [/c] [/l] [/q] – This applies the stored DACLs to the specified directory from the ACL file.
[/setowner<username> [/t] [/c] [/l] [/q]] – alters the matching file’s owner to the new one
[/findsid<sid> [/t] [/c] [/l] [/q]] – looks up files with a DACL matching the specified SID
[/verify [/t] [/c] [/l] [/q]] – This command basically checks for non-canonical ACLs or with inconsistent lengths with ACE (Access Control Entry) counts.
[/reset [/t] [/c] [/l] [/q]] – Substitutes ACLs for matching files with default ACLs
[/grant[:r] <sid>:[…]] – Changes access rights for specified user.
Parameter Breakdown:
- /t – for files in the current directory and its subdirectories.
- /c – ignores file errors during operation (errors messages are still shown).
- /l – for symbolic links (instead of destination)
- /q – suppress the success messages
How to identify icacls.exe as a virus?
Often malware programmers mask services and system files as malware to deceive security programs and scans. Ensure the EXE file is at the mentioned path and the size does not vary significantly.
You can verify the process’s running status from Task Manager. Ensure that it is not consuming too much memory or CPU power.
Resolving issues regarding icacls.exe
We recommend keeping up-to-date Windows for security reasons and hardware driver updates. Install a well-reviewed third-party antivirus program or malware remover to detect and repair any threats automatically.
You can also run system scans using the following commands in the command prompt window:
- cleanmgr
- sfc/scannow
Maintain your computer by removing files and programs you no longer require. You can also enable Windows and check the autostart programs using MSConfig.
As a good practice, create Restore Points to preserve the state of your system before making changes. In case a runtime error occurs, you can revert or reset to a previous point.
Here are the commands you may use to restore your PC:
- resmon command
- DISM.exe/Online/Cleanup-image/Restorehealth
Both options allow you to identify faulty processes and restore the Operating System without losing data. However, it is best to backup your files before committing to any changes.
As alternatives, you may resort to anti-malware software and third-party antivirus programs to detect hidden processes and potential spyware or Trojans, which the system scans can overlook. Here is how to enable or disable Windows Defender in case if you are using any 3rd party antivirus program. Find yourself a decent package that can detect and remove sleeping malware and viruses from your hard drive.


