The forfiles.exe utility by Microsoft Windows is responsible for selecting and running commands on files, more commonly with batch files. Some of the file selection criteria include name and last modified date, but the command specifier utilizes some special parameters. While it was introduced as an add-on in earlier versions of the Windows operating systems, it became a regular utility with Windows Vista.
Quick Overivew
File Size and Location
Forfiles.exe can be located in the C:\Windows\System32\ folder and it can be identified as Win32 file type. The executable usually takes up around 48 KB of space.
This is what an authentic forfiles.exe file looks like in Windows 10 PC / Laptop:

Quick Overview
File Name: forfiles.exe
File Description: ForFiles – Executes a command on selected files
Type: Executable Application
File Size: 40 KB
File Version: 10.0.15063.0 (WinBuild.160101.0800)
Product Name: Microsoft® Windows® Operating System
Copyright: Microsoft Corporation
Language: English
What is Forfiles.exe
Forfiles.exe is a useful command-line tool that is commonly used by the system administrator. This allows you to execute a command for particular or multiple files.
Is Forfiles.exe a Malware?
Remember that malware often disguises itself as genuine executable programs such as forfiles.exe so do ensure that you acquire your device installation program from an official vendor. If you think that your forfiles.exe file is a Trojan virus, remember to check its location. If it is found in any place other than its designated location, it may be a virus.
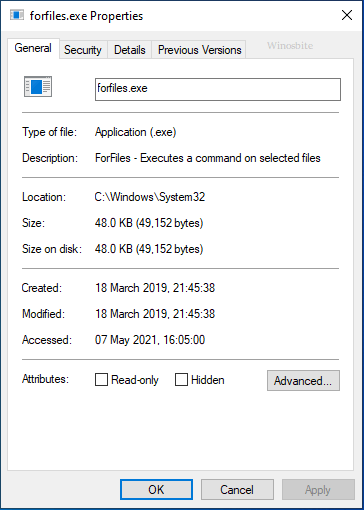
Go to the C:\Windows\System32\ folder, right-click on forfiles.exe and select properties. If it shows blow information like ‘ForFiles – Executes a command’ on selected files and other similar detail as shown below then it is not a virus or malware.
How to Fix Forfiles.exe Startup Errors
Few users have complained that they are receiving errors during the startup of Windows 10. During this time the system screen may freeze or show a blank screen for a while. In such a case, follow the below steps:
1) Open Run command with Admin access
2) Type sfc /scannow and click on the Enter key
3) Let the system scan and repair if there is any damaged file
4) When finish then restarts the system.
If you are still receiving error then may run below command line one after another and restart the PC/Laptop:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Scanhealth
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth12
DISM.exe /online /cleanup-image /startcomponentcleanup
Sample Command Lines
forfiles [/P pathname] [/M searchmask] [/S] [/C command] [/D [+ | -] [{<date> | <days>}]]
(i) /P <pathname>: Details the path from which the search is to commence. The default command states that searching is to start in the current operational directory.
(ii) /M <searchmask>: This command searches files corresponding with the denoted search mask. * is the default search mask.
(iii) /S: Directs the for files command to search in the subdirectories repetitively and selects matching files consequently.
(iv) /C <command>: Processes the allotted command on each file respectively and the command strings must be enclosed in double-quotes. “cmd / c echo @file” is the default command string.
- @file: The name of the file.
- @filename: The name of the file, not including the file extension.
- @ext: The file extension is double-quoted. The last extension is sent, only if a file has several extensions, and an empty string is sent if a file is lacking an extension.
- @path: The file’s full path is sent, along with the drive letter and the file extension.
- @relpath: The file’s path relative to the starting directory is returned.
- @isdir: By default, this variable evaluates a string to FALSE. However, it is TRUE if the file type is categorized as a directory.
- @fsize: Returns the file size in bytes. Directories are automatically 0.
- @fdate: Date at which the file was last modified.
- @ftime: Time at which the file was last modified.
(v) /D [{+\|-}][{<date> | <days>}]: Chooses files depending upon the date they were last modified. Can be denoted either by the MM/DD/YYYY format or by the number of days from 0-32,768.
If the <date>is preceded with a ‘-‘ sign, all the files modified before or on the specified date are selected. Else, the files modified on and after that date are selected.
Similar Files:
StartMenuExperienceHost.exe, Pcalua.exe, ehshell.exe, Gfxui.exe

