This computing giant’s journey started over two decades from now. In an era when technology backed events such as the AI was a Utopian dream. Bill Gates and Paul led on to create the globe’s most favoured and followed tech company, Microsoft. That launched the world’s first ever personal computer (PC). On, November 10, 1983, Bill Gates officially announced Microsoft Windows. Now a trusted computing brand amongst millions of users.
In its initial years, Windows was a simple disk operating system or shortly known the MS DOS, comprising a graphical user interface.
Later on in 1990, the company launched a brand new product line. Including a full range of modern operating systems with their individual code-bases. And the rest as they say it has made history and it continues to build on.
Let’s take a glimpse of how the operating systems have drastically improved over the years post MS DOS.
Windows 1.0 | Release Year: 1985-1992
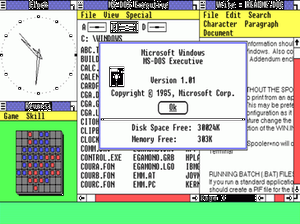 The tale behind Windows’ nomenclature associates with the main coding technique. Before becoming relevant, the project was code named as Interface Manager. Then launched to consumers as ‘Windows’ based on the windowing system. As the computing boxes called windows formed an integral part of the system.
The tale behind Windows’ nomenclature associates with the main coding technique. Before becoming relevant, the project was code named as Interface Manager. Then launched to consumers as ‘Windows’ based on the windowing system. As the computing boxes called windows formed an integral part of the system.
The new OS allowed users to point and click items on the screens as opposed to typing MS-DOS commands. What we now call as apps were then called gadgets. And these native gadgets viz a viz calendar and calculator became an instant hit amongst users! The 1985 model included the very first version of MS Paint. Which as we know it, in 2018, became obsolete. The first Windows OS also hosted a primitive word processor.
Windows 2.0 | Release Year:1987
 The second version of Windows released in 1987 turned out to just be an extension of its forerunner. Although it was much more popular in spite of not having a host of changes. One of which being the addition of a “runtime version”. With new graphical applications such as Word and Excel.
The second version of Windows released in 1987 turned out to just be an extension of its forerunner. Although it was much more popular in spite of not having a host of changes. One of which being the addition of a “runtime version”. With new graphical applications such as Word and Excel.
It had real-mode memory, which expanded up to 1 megabyte of memory. Because of which it could run under the agile DESQview that comprised the 286 protect mode.
The Windows 2.0 version also caught a lot of buzz for a lawsuit filed by Apple. For mimicking the look and feel of their operating system. However, all the charges were dropped by Judge William Schwarzer. Except 10 out of the 189 filed by Apple under the copyright infringement act.
Windows 3.0 | Release Year: 1990
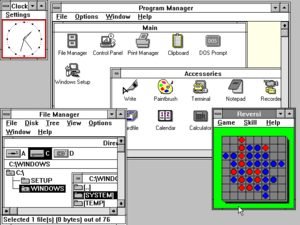 Better icons. Better performance. Advance graphics with 16 colors made for Intel 386 processors. Doesn’t the third version of windows appear promising in an era when few owned personal computers?
Better icons. Better performance. Advance graphics with 16 colors made for Intel 386 processors. Doesn’t the third version of windows appear promising in an era when few owned personal computers?
The third Windows OS came with enhanced functionalities for the native applications. Allowed users to work faster with older MS-DOS software by introducing virtual memory.
Although, Windows 3.0’s standard design gained popularity for Microsoft over the years. 3.0 comprised a host of apps. Such as Program Manager, File Manager, Print Manager and Games(Hearts, Minesweeper and Solitaire)!
Windows NT 31. – 4.0 | Release Year: 1993-1996
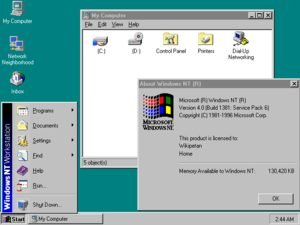 Windows NT (New Technology) was a 32-bit operating system that supported preemptive multitasking. The main drawback here was increasing programming difficulty caused by poor driver support. Thus driving programmers to stop from catering to the smaller market segment.
Windows NT (New Technology) was a 32-bit operating system that supported preemptive multitasking. The main drawback here was increasing programming difficulty caused by poor driver support. Thus driving programmers to stop from catering to the smaller market segment.
Although, the version worked wonders for bigger, high-end machines. As they offered the hardware and resources essential for 3.x’s functionality.
Windows 95 | Release Year:1995
 With a major upgrade, the 1995 Windows was the star of operating systems. Especially, over its predecessor Windows 3.0.
With a major upgrade, the 1995 Windows was the star of operating systems. Especially, over its predecessor Windows 3.0.
It’s new user interface hosted several crucial software improvements. One of which was the 32-bit upgrade from the meagre 16-bit version.
This meant more speed, more accuracy for human tasks.
Along with a revamped processing, deletion of previous Windows and DOS applications nullified glitches that i older versions failed to. Like the 640K central memory, 8-character file names amongst others. Another set of features that need a mention include the OS’ smartness to auto detect and configure additionally installed hardware. For example the ability to plug and play other devices.
Windows 98 | Release Year: 1998
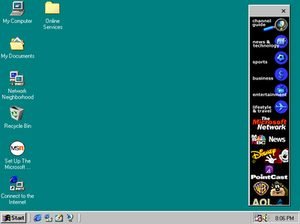 Bringing in faster, futuristic technology to the table was the Windows 98. That honed some spectacular and massive changes. The inclusion list consisted FAT32, AGP, MMX, USB, DVD and ACPI. Out of which the Internet Connection Sharing was the most prominent change. Its network address translation allowed multiple PCs connected through LAN share internet with each other.
Bringing in faster, futuristic technology to the table was the Windows 98. That honed some spectacular and massive changes. The inclusion list consisted FAT32, AGP, MMX, USB, DVD and ACPI. Out of which the Internet Connection Sharing was the most prominent change. Its network address translation allowed multiple PCs connected through LAN share internet with each other.
However, for a user this addition didn’t bring much of change. As accessing a document from their personal hard disk was easier than through a web server across the globe.
Windows 2000 | Release Year: 2000
 Hip product labelling continues with the Windows 2000 or as they call it W2K! This version was for server and workstation markets. That often used the Internet, intranet and additional devices like printers.
Hip product labelling continues with the Windows 2000 or as they call it W2K! This version was for server and workstation markets. That often used the Internet, intranet and additional devices like printers.
In all Microsoft launched four Windows 2000 OS versions. Professional (for business desktop and laptop systems), Server (both a Web server and an office server), Advanced Server (for line-of-business applications) and Data-center Server (for high-traffic computer networks).
Many features of the Windows 98 were retained in the 2000 OS. These included Device Manager, WMP, and an updated DirectX supporting modern gaming.
Windows ME – Millennium Edition | Release Year: 2000
 Last of the DOS-based kind, the Windows ME (short for Windows Millenium) was next-in-line to the 98 model. Its novelty lied in the new multi-media editing application – Windows Makers; a standard IE 5.5 browser and Windows Media Player 7.
Last of the DOS-based kind, the Windows ME (short for Windows Millenium) was next-in-line to the 98 model. Its novelty lied in the new multi-media editing application – Windows Makers; a standard IE 5.5 browser and Windows Media Player 7.
The ME version also offered the first ever System Restore feature. Through which the operating system could restore system files to previous date and time.
Windows XP | Release Year: 2001
 Codename Whistler AKA Windows XP came with a number of editions. Each with set of features pertaining to a particular type of consumer segment.
Codename Whistler AKA Windows XP came with a number of editions. Each with set of features pertaining to a particular type of consumer segment.
Popular editions include: Windows XP Home Edition, Windows XP Professional, Windows XP Media Centre Edition, Windows XP Starter Edition among others.
What Microsoft really assured in this line-up was the mobile plug and play feature. So one could easily connect to WiFi. The OS included 802.11x wireless security standard, which was one of the reasons why it topped the best-seller chart.
Windows Vista | Release Year: 2006
 In 2006 Windows introduced a new restricted user mode – User Account Control in Windows Vista. That turned out to be an advanced, reliable, user-friendly, secure product. To both the business and home consumer segment.
In 2006 Windows introduced a new restricted user mode – User Account Control in Windows Vista. That turned out to be an advanced, reliable, user-friendly, secure product. To both the business and home consumer segment.
It came in 6 editions: Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Business, Enterprise and Ultimate. Windows Vista could detect basic hardware problems in initial stages. The OS’s processing and start-up was much faster than 95 and XP. And it consumed significantly less power!
The version featured new graphics, the Windows Aero GUI, new applications (such as Windows Calendar, Windows DVD Maker, and new games: Chess, Mahjong, and Purble Place. Not to forget, a new web browser – Internet Explorer 7, Windows Media Player 11, and a large number of underlying architectural changes.
Windows 7 | Release Year: 2009
 Blackcomb, Vienna, Windows 7. Next to Windows Vista, Windows 7 provided faster booting, device stage, Windows PowerShell, a better UAC, multi-touch, IE8 and improved settings! It came in 6 editions just like Windows Vista.
Blackcomb, Vienna, Windows 7. Next to Windows Vista, Windows 7 provided faster booting, device stage, Windows PowerShell, a better UAC, multi-touch, IE8 and improved settings! It came in 6 editions just like Windows Vista.
At the Windows 7 launch the company also presented the Windows Server 2008 R2, which was a counterpart to the Windows 7’s server.
In last week of March 2019, the Microsoft announced that there won’t be any new update and windows 7 is going to be closed.
Windows 8 | Release Year: 2012
 Jump to the future – Windows 8 was like no other PC’s OS. Redesigned for an era that craved touch-screens, and instant access in a PC that met the needs of tomorrow.
Jump to the future – Windows 8 was like no other PC’s OS. Redesigned for an era that craved touch-screens, and instant access in a PC that met the needs of tomorrow.
In Windows 8, Microsoft introduced an updated Start menu or the Start screen depicting Live Tiles. That linked users to respective applications, real-time updates, and a full-screen application platform. The new beast could boot up faster than Windows 7. Provided USB 3.0 ports, Windows Store and the flexibility of running from USB drives with Windows To Go and more.
The OS’ dynamism made it run on both x86 PCs and ARM processors.
Windows 10 | Release Year: 2015
 To cruise-control a not so popular Windows 8 OS, Microsoft engineers burned the midnight oil to reveal the first preview of “Threshold” (Windows 10) in the year 2014. Later on, officially launching the beta version starting 2015. Everything was grand about the latest version. From quicker startup and resume, built-in security and an expanded Start Menu. This version gave users their very own digital personal assistant – Cortana. Microsoft Edge instead of the old IE web browser. The choice to view Windows Store apps as a window. Revamped core apps, Continuum, and a compact Settings App.
To cruise-control a not so popular Windows 8 OS, Microsoft engineers burned the midnight oil to reveal the first preview of “Threshold” (Windows 10) in the year 2014. Later on, officially launching the beta version starting 2015. Everything was grand about the latest version. From quicker startup and resume, built-in security and an expanded Start Menu. This version gave users their very own digital personal assistant – Cortana. Microsoft Edge instead of the old IE web browser. The choice to view Windows Store apps as a window. Revamped core apps, Continuum, and a compact Settings App.
Microsoft also offered the chance to any and all devices supporting Windows to upgrade their old OS to Windows 10. Even to devices running pirated old Windows OS!
Windows 10 OS Updates | Release Year: 2017
Cortana, the personal assistant did more than we thought. For example it helped users setup windows with voice commands. This feature made the setting-up process 10x simpler. As compared to the age old Windows Vista style.
Windows 10, 2017 offered variations in gaming mode and picture-in-picture support to Universal Windows Apps. A cool new Dubbed Night Light. That let Windows 10 reduce blue light on the screen after sundown. Paint 3D brought in a 3D outlook the premier paint app. And big time improved control updates. Which meant users could pause installing updates for a week. And extend the active working till upto 18 hours a day.
Windows 10 OS Updates | Release Year: 2018
In addition to the largely liked OS of the decade, Redstone5 Windows 10 2018 updates brought in spectacular changes. Top ones include clipboard history and the much-anticipated File Explorer dark theme.
It update also included: “Your Phone” app. Where users can connect their smartphone to the Windows desktop. The app let users type into their phone through the PC. Send, share access photos on devices interchangeably.
The Redstone5 version also offered a new Sets feature. Wherein users could not just combine tabs from different applications in one window. But also drag and drop between each tab using a simple shortcut: Ctrl + Windows + Tab.
The most novel out of the lot was Windows’ machine learning auto restart update. This update predicted the times your laptop went on standby, and put it to restart smartly. This feature is customizable to users’ preferences. So that your computer doesn’t restart when in use for for longer periods. Isn’t that cool?
Microsoft Operating Systems for Servers
After the successful launch of OS’ for personal computers, it was only seeming for Microsoft to innovate new product segments. So, the world saw the rise of Operating Systems once again for services and handheld devices.
Windows Server | Release Year: 2003
Windows Servers was a series of server operating systems. They were much more stronger than its desktop operating system contraries. The server came with a “Manage Your Server” wizard. That made machine configurations for specific roles simpler, and amplified performance. Windows Server was efficient in corporate networking, Internet/Intranet hosting, databases, and enterprise-scale messaging.
Additionally, the brand also launched Windows Server 2003 R2. An updated version of Windows Server 2003 in December 2005.
Windows Home Server | Release Year: 2007
Designed to connect many computers at home, Microsoft launched the Windows Home Server in January 2007. Using the server consumers could share digital photos, media files and automatically backup the home network computers. Through Windows Media Connect, WHS also let consumers transfer files saved on the server to other compatible devices.
Windows Home Server 2011 | Release Year: 2011
Released in April 2011, WHS 2011 was a major segment release built on the Windows Server 2008 R2 code. This version did not contain the Drive Extender drive pooling technology seen in the premier Windows Home Server. It supported x86-64 hardware only.
Windows Server 16 | Release Year: 2016
Later in September 2016, Microsoft Windows released the Windows Server Operating System. After a first unveiling in September 2014. The official launch at Microsoft Ignite Conference witnessed a large confluence of tech enthusiasts for the brand’s latest OS venture.
Windows’ legacy has been that of ponders and wonders, and we can only anticipate what the future holds. According to you, how will Windows’ computing tech improve our lives in the coming years?